Working with CSV Files
The comma-separated-value (CSV) file format is used as the basis of data transfer operations, and is supported by all spreadsheet and database applications. The following file types are supported for import and export:
- Import:
CSVandZIP(a compressed CSV file) - Export:
CSV
Important! We recommend that you use a program that supports UTF-8 encoding, such as Notepad++ or OpenOffice Calc, to edit CSV files. Microsoft Excel inserts additional characters into the column header of the CSV file, which can prevent the data from being imported back into Magento. If you work on the Mac, you can save your data in the CSV (Windows) format.
CSV files have a specific structure that must match the database. Each column heading corresponds to the Attribute Code of the field that is represented by the column. To ensure that the column headings can be read by Magento, first export the data from your store as a CSV file. You can then edit the data and re-import it into Magento.
If you open an exported CSV file in a text editor, you will see that values are separated by commas, and multiple values are enclosed in double-quotes. During import, you can specify a custom separator character, although a comma is the default.
Product CSV Structure
A full export of the product database contains information about each product in the catalog, and the relationships between them. Each record has fixed selection of columns that corresponds to the attributes in the catalog, although the order of the attributes is ignored during the import process.
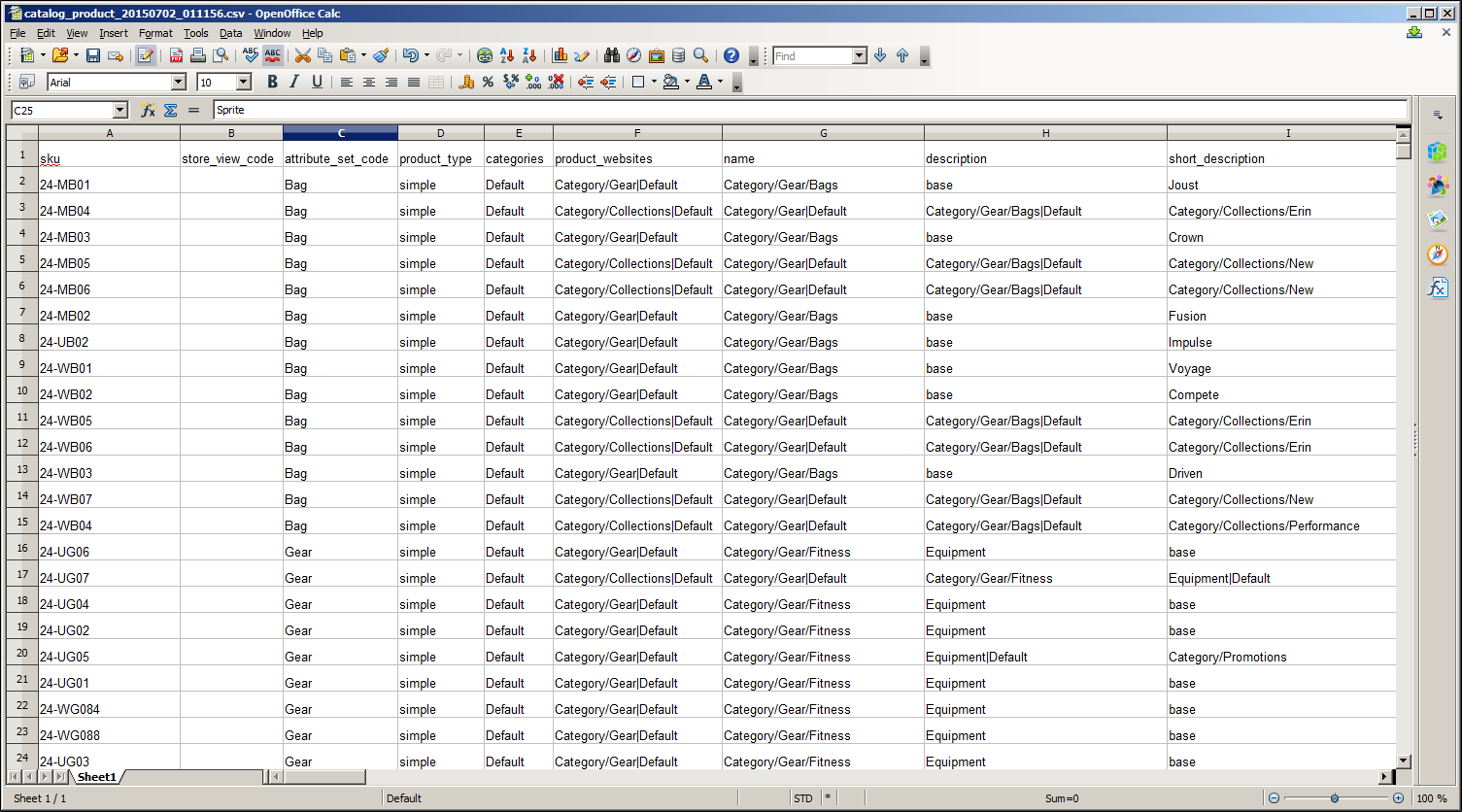 Exported Product CSV in OpenOffice Calc
Exported Product CSV in OpenOffice Calc
The first row of the table contains the names of each attribute, which are used as column headers. The remaining rows describe the individual product records. Any row that begins with a value in the SKU column is the beginning of a new product record. A single product might include several rows that contain information about multiple images or product options. The next row that has a value in the SKU column begins a new product.
The category column contains a path for each category to which the product is assigned. The path includes the root category, followed by a forward slash (/) between each level. By default, the pipe “|” character is used to separate different category paths. For example:
Default Category/Gear|Default Category/Gear/Bags.
To import data, you need to include only the SKU and any columns with changes. Any blank columns are ignored during the import process. It is not possible to add attributes during the import process. You can include only existing attributes.
For a detailed description of each product attribute, see Product CSV File Structure.
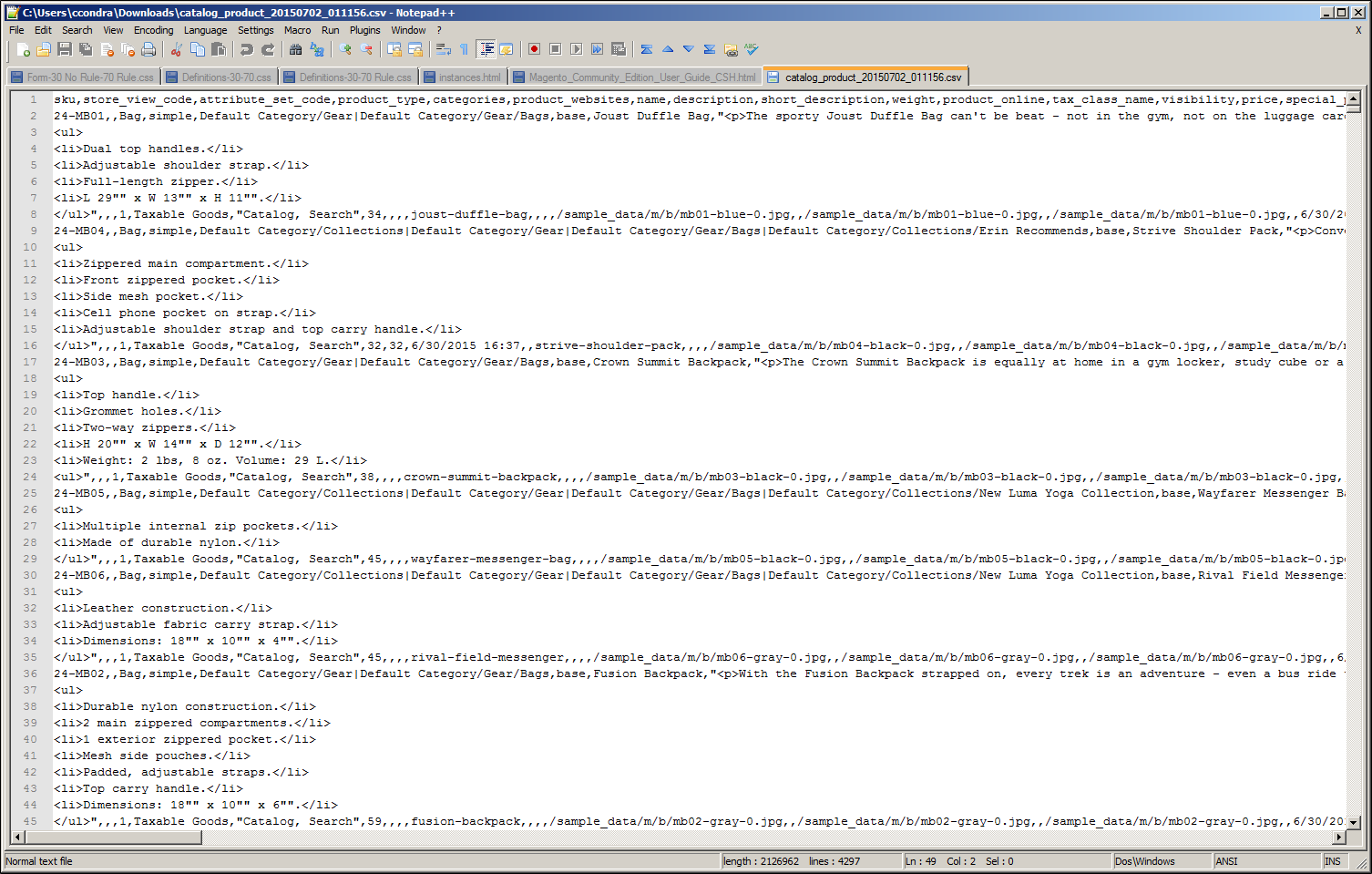 Exported Product CSV in Notepad++
Exported Product CSV in Notepad++
CSV Product Structure
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
_<name> |
Column headers that begin with an underscore contain service entity properties or complex data. Service columns are not product attributes. |
<attribute_name> |
Column headers with an attribute code or field name identify the column of data. A column might represent a system attribute, or one that was created by the store administrator. |
Customer CSV Structure
The customers CSV file contains customer information from the database, and has the following structure:
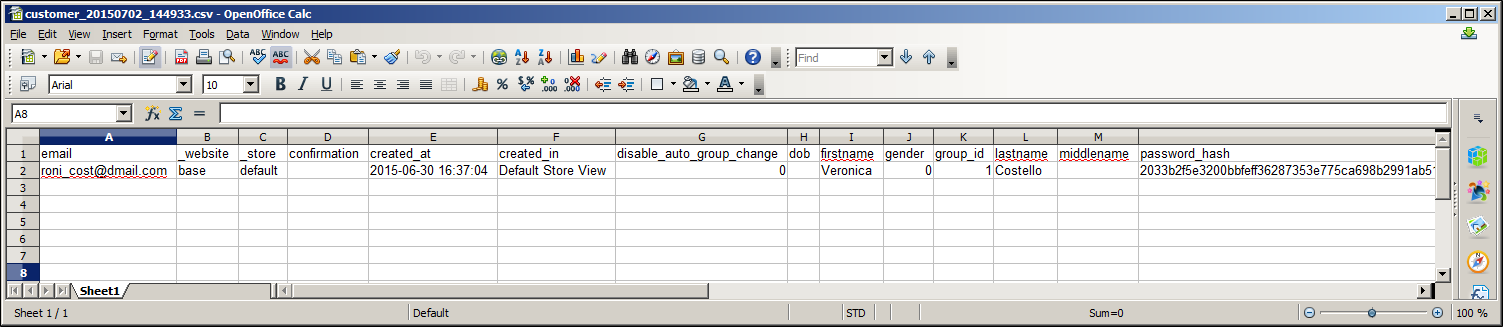 Exported Customer CSV in OpenOffice Calc
Exported Customer CSV in OpenOffice Calc
The first row of the table contains the names of the attribute columns (which are the same as attribute codes). There are two types of column names, as shown in the following table. Other rows contain attribute values, service data, and complex data. Each row with non-empty values in the email and _website columns starts the description of the subsequent customer. Each row can represent customer data with or without address data, or the address data only. In case a row contains only the address data, values in the columns, related to the customer profile, will be ignored and may be empty.
To add or replace more than one address for a customer, in the import file add a row for each new address with empty customer data and the new or updated address data below the customer data row.
For a detailed description of each customer attribute, see Customer CSV File Structure.
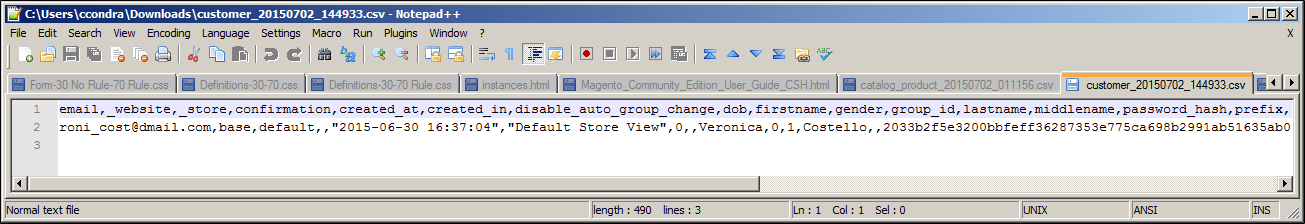 Exported Customer CSV in Notepad++
Exported Customer CSV in Notepad++
CSV Customer Structure
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
_<name> |
Column headers that begin with an underscore contain service entity properties or complex data. Service columns are not customer attributes. |
<attribute name> |
The names of the columns with values of both system-created attributes, and attributes created by the store administrator. |