Layout overview
What’s in this topic
This article describes the basic concepts you need to know to create layouts for your custom theme.
Introduction
In Magento, the basic components of page design are layouts, containers, and blocks. A layout represents the structure of a web page (1). Containers represent the placeholders within that web page structure (2). And blocks represent the UI controls or components within the container placeholders (3). These terms are illustrated and defined below.
The objective is to create a structured, common set of layout instructions to render pages. Most pages on a website can be categorized as a 1 column, 2 column, or 3 column layout. These page layouts can be applied to a page from within the admin panel.
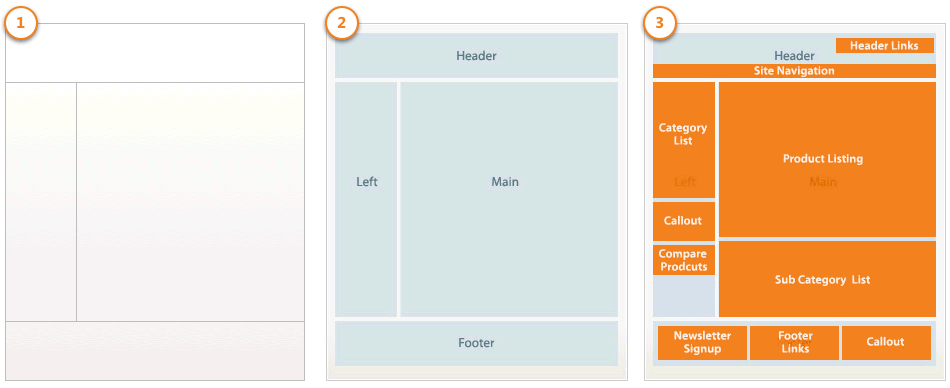
(1) Layouts provide the structures for web pages using an XML file that identifies all the containers and blocks composing the page. The details of layout XML files are described later in this section.
(2) Containers assign content structure to a page using container tags within a layout XML file. A container has no additional content except the content of included elements. Examples of containers include the header, left column, main column, and footer.
(3) Blocks render the UI elements on a page using block tags within a layout XML file. Blocks use templates to generate the HTML to insert into its parent structural block. Examples of blocks include a category list, a mini cart, product tags, and product listing.
Purpose of page layouts
The purpose of page layouts is to create a structured, common set of layout instructions to render pages. Most pages on a website can be categorized as fitting into a 1, 2, or 3-column container system. These page layouts can be selected in the admin panel to provide a specific layout per page.
Basic layouts
The basic view of all Magento storefront pages is defined in two page configuration layout files located in the Magento_Theme module:
<Magento_Theme_module_dir>/view/frontend/layout/default.xml: defines the page layout.<Magento_Theme_module_dir>/view/frontend/layout/default_head_blocks.xml: defines the scripts, images, and meta data included in pages’<head>section.
These basic page configuration layouts are extended in other Magento modules and in Magento themes.
You can also extend or override these files in your custom theme.
Layout handles
A layout handle is a uniquely identified set of layout instructions that serves as a name of a layout file.
There are three kinds of layout handles:
- page-type layout handles – Synonyms of the page type identifiers. Correspond to “full action names” of controller actions, for example, catalog_product_view.
- page layout handles – Identifiers of specific pages. Correspond to controller actions with parameters that identify specific pages, for example, catalog_product_view_type_simple_id_128 or for a CMS page, cms_page_view_id_home.xml.
- arbitrary handles - Do not correspond to any page type, but other handles use them by including.
Layout files types and conventions
Layout file types: by role
For a particular page, its layout is defined by two major layout components: page layout file and page configuration file (or generic layout for pages returned in AJAX requests, emails, and so on).
Following are the definitions of each layout file type:
- Page layout: an XML file declaring a page wireframe inside the
<body>section of the HTML page markup, for example, two-column page layout. - Page configuration: an XML file declaring detailed structure, contents and meta-information of a page (includes the
<html>,<head>, and<body>sections of the HTML page markup). - Generic layout: an XML file declaring page detailed structure and contents inside the
bodysection of the HTML page markup. Used for pages returned by AJAX requests, emails, HTML snippets, and so on.
For details, refer to Layout file types.
In this guide we use layout files when talking about concepts which are similarly applied to all of these types of layout files.
Module and theme layout files
The following terms are used to distinguish layouts provided by different application components:
- Base layouts: Layout files provided by modules. Conventional location:
- Page configuration and generic layout files:
<module_dir>/view/frontend/layout - Page layout files:
<module_dir>/view/frontend/page_layout
- Page configuration and generic layout files:
- Theme layouts: Layout files provided by themes. Conventional location:
- Page configuration and generic layout files:
<theme_dir>/<Namespace>_<Module>/layout - Page layout files:
<theme_dir>/<Namespace>_<Module>/page_layout
- Page configuration and generic layout files:
Customize layout
To ensure stability and secure your customizations from being deleted during upgrade, do not change out-of-the-box Magento module and theme layouts. To make the necessary changes, create extending and overriding layout files in your custom theme.
Layout files processing
The Magento application processes layout files in the following order:
- Module base files loaded.
- Module area files loaded.
- Collects all layout files from modules. The order is determined by the modules order in the module list from the
app/etc/config.phpfile. (If their priorities are equal, they are sorted according to their alphabetical priority.) - Determines the sequence of inherited themes
[<parent_theme>, ..., <parent1_theme>] <current_theme> -
Iterates the sequence of themes from last ancestor to current:
a. Adds all extending theme layout files to the list.
b. Replaces overridden layout files in the list.
- Merges all layout files from the list.
Layout files that belong to inactive modules or modules with disabled output are ignored.
Layout files validation
After layouts are merged, Magento validates them.
Layout validations and error handling depends on the application mode in which your Magento instance runs:
-
developer mode: syntax is validated in
.xmland.xsdfiles, and.xmlfiles are validated according to the xsd schema. If any validation fails, the hard failure with process halt occurs. -
production or default modes: syntax is validated in
.xmland.xsdfiles. If validation fails, errors are logged to thevar/logdirectory without throwing an exception. The validation according to the xsd schema is not performed.