Adding a custom indexer
Adding a custom indexer
This topic discusses how to create a custom indexer. We’ve recently made a performance improvement that enables you to declare one or more shared indexers; if one of the shared indexes is already up-to-date, it doesn’t need to be reindexed.
To implement your own indexer, add the following code in your module:
Custom indexer logic
Your custom indexer class should implement \Magento\Framework\Indexer\ActionInterface, and the indexer should be able to perform three types of operations:
- Row reindex: processing a single entry from a dictionary; responsibility of
executeRow($id) - List reindex: processing a set of dictionary entries; responsibility of
executeList($ids), where$idsis an array of entity IDs - Full reindex: processing all entities from a specific dictionary; responsibility of
executeFull()
Indexer configuration
Declare a new indexer process in the etc/indexer.xml file with the following attributes:
| Attribute | Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|
id |
Yes | A unique indexer ID |
class |
No | The class that processes indexer methods (executeFull, executeList, executeRow) |
primary |
No | The source provider |
shared_index |
No | Use this option to improve performance if your indexer is related to another indexer. In this example, if the Catalog Product Rule index needs to be reindexed, but other catalog product rule indexes are up-to-date, then only the Catalog Product Rule is reindexed. |
view_id |
No | The ID of the view element that is defined in the mview.xml configuration file. |
For example,
1
2
3
4
5
6
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:Indexer/etc/indexer.xsd">
<indexer id="design_config_grid" view_id="design_config_dummy" class="Magento\Theme\Model\Indexer\Design\Config" primary="design_config">
...
</indexer>
</config>
An indexer process can also have the following optional parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
description |
The description of indexer to be displayed on the System > Tools > Index Management page. |
fieldset |
Describes the fields, source, and data provider of the flat index table. |
saveHandler |
An extension point. The class for processing (deleting, saving, updating) items when indexing. |
structure |
The class that processes (creates, removes) flat index tables. |
title |
The title of indexer to be displayed on the System > Tools > Index Management page. |
For example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:Indexer/etc/indexer.xsd">
<indexer ...>
<title translate="true">Design Config Grid</title>
<description translate="true">Rebuild design config grid index</description>
<fieldset name="design_config" source="Magento\Theme\Model\ResourceModel\Design\Config\Scope\Collection"
provider="Magento\Theme\Model\Indexer\Design\Config\FieldsProvider">
<field name="store_website_id" xsi:type="filterable" dataType="int"/>
<field name="store_group_id" xsi:type="filterable" dataType="int"/>
<field name="store_id" xsi:type="filterable" dataType="int"/>
</fieldset>
<saveHandler class="Magento\Framework\Indexer\SaveHandler\Grid"/>
<structure class="Magento\Framework\Indexer\GridStructure"/>
</indexer>
</config>
All indexers related to a module should be declared in one file.
MView configuration
Add the mview.xml configuration file in the etc module directory, where you declare the following:
- indexer view ID
- indexer class
- the database tables the indexer tracks
- what column data is sent to the indexer
All Mview declarations related to a module should be declared in one file.
Example of a custom indexer implementation
To push best-selling products to the top of a category listing, process statistics about sales to change the product position dynamically.
Assuming your module is named <VendorName>_Merchandizing, you must write the appropriate code in the indexer class Merchandizing/Model/Indexer/Popular.php
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
<?php
namespace <VendorName>\Merchandizing\Model\Indexer;
class Popular implements \Magento\Framework\Indexer\ActionInterface, \Magento\Framework\Mview\ActionInterface
{
/*
* Used by mview, allows process indexer in the "Update on schedule" mode
*/
public function execute($ids){
//Used by mview, allows you to process multiple placed orders in the "Update on schedule" mode
}
/*
* Will take all of the data and reindex
* Will run when reindex via command line
*/
public function executeFull(){
//Should take into account all placed orders in the system
}
/*
* Works with a set of entity changed (may be massaction)
*/
public function executeList(array $ids){
//Works with a set of placed orders (mass actions and so on)
}
/*
* Works in runtime for a single entity using plugins
*/
public function executeRow($id){
//Works in runtime for a single order using plugins
}
}
Next, declare the indexer in Merchandizing/etc/indexer.xml:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:Indexer/etc/indexer.xsd">
<indexer id="merchandizing_popular" view_id="merchandizing_popular_order" class="Vendor\Merchandizing\Model\Indexer\Popular">
<title translate="true">Popular Products</title>
<description translate="true">Sort products in a category by popularity</description>
</indexer>
</config>
In this file, declare a new indexer process with the attribute:
id- To identify this indexer. Check status, mode or reindex this indexer by command line.view_id- Id of view element which will be defined in themviewconfiguration file.class- The name to the class which we process indexer method.
Finally, declare the indexer view (merchandizing_popular_order) that tracks sales (Merchandizing/etc/mview.xml):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<config xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="urn:magento:framework:Mview/etc/mview.xsd">
<view id="merchandizing_popular_order" class="Vendor\Merchandizing\Model\Indexer\Popular" group="indexer">
<subscriptions>
<table name="sales_order" entity_column="entity_id" />
</subscriptions>
</view>
</config>
These settings start <VendorName>\Merchandizing\Model\Indexer\Popular::execute method every time an order is changed.
After this, please refresh the cache and go to System > Tools > Index Management through the Admin to verify the custom indexer result.
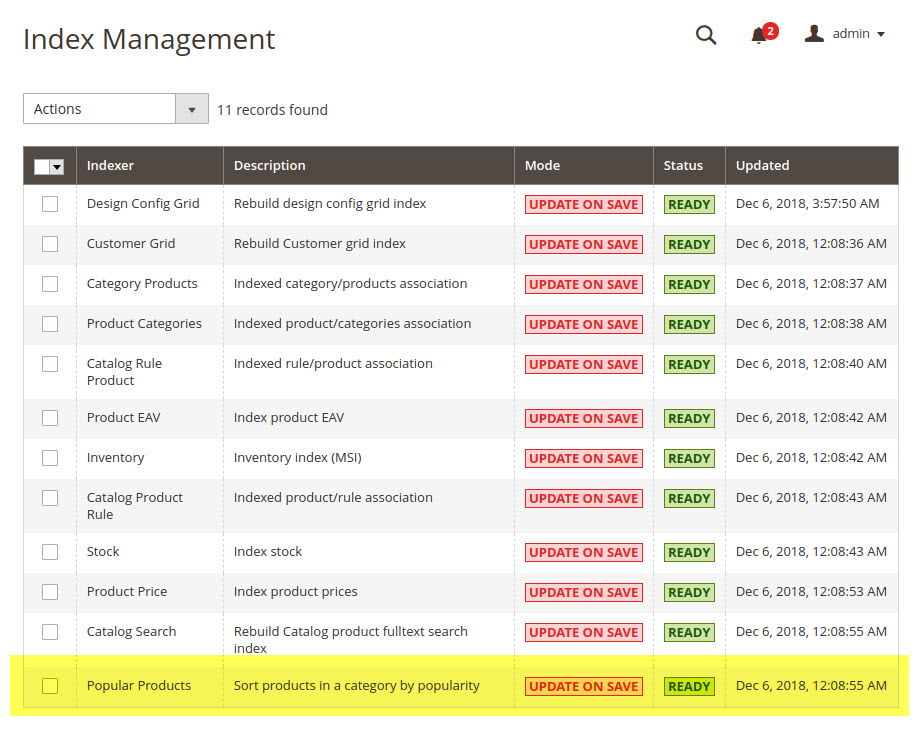
Now when an order is placed, the Popular Products indexer calculates the sorting order of the products by popularity and stores this data in the index table, so that it can be used in product displaying logic.
Use the following command to reindex the custom indexer:
1
bin/magento indexer:reindex merchandizing_popular
Use the following command to invalidate the custom indexer:
1
bin/magento indexer:reset merchandizing_popular